Infrastructure monitoring forms the backbone of modern IT operations. It keeps your systems running smoothly, preventing costly downtime and ensuring optimal performance but what exactly does it entail, and why is it crucial for your organization? This article dives deep into the world of infrastructure monitoring, exploring its components, benefits, and best practices.
Understanding Infrastructure Monitoring: Definition and Importance
Infrastructure monitoring is essential for tracking, analyzing, and managing the performance, availability, and health of your entire IT environment—from physical servers to cloud services. It ensures that every component runs smoothly and efficiently, and this process goes beyond simply keeping things operational; it’s about proactively identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By continuously monitoring your infrastructure, you can catch these issues early, ensuring minimal disruption and optimal system performance.
The scope of infrastructure monitoring is vast. It includes:
- Servers (physical and virtual): This category includes both on-premises physical servers and virtual servers hosted in the cloud or data centers. Physical servers are tangible machines that run your applications and store data, while virtual servers are software-based instances that simulate physical servers, providing flexibility and scalability in cloud environments.
- Networks: This encompasses all communication pathways that connect your systems, from local networks to wide-area networks. Effective network monitoring ensures smooth and uninterrupted data transmission, helping to identify and resolve issues like latency, packet loss, or connectivity problems.
- Storage systems: Storage systems encompass a range of physical and virtual platforms used for data storage. These include local storage devices such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) within server infrastructure, network-attached storage (NAS) systems for shared access to data repositories, and cloud-based storage solutions, offering scalable and often cost-effective data storage capabilities. Proactive monitoring and management of these systems are crucial to ensure adequate capacity, optimal performance, and the accessibility and security of mission-critical data.
- Cloud services: Monitoring the health and performance of services hosted in the cloud—whether infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), or software-as-a-service (SaaS)—involves tracking their availability, performance, and resource usage to ensure they meet your business needs.
- Applications: This includes monitoring the performance and functionality of software applications used by your business. It involves tracking metrics like response times, error rates, and user interactions to ensure that the applications operate efficiently and provide a positive user experience.
By keeping a watchful eye on these components, you can:
- Prevent downtime: Continuous monitoring helps catch potential issues early, preventing them from escalating into major problems that could lead to system failures. For instance, spotting an unusual spike in CPU usage or network traffic allows you to address these issues before they cause unplanned outages, keeping your systems running smoothly.
- Optimize performance: Effective monitoring helps you identify and resolve bottlenecks and inefficiencies in your infrastructure. By analyzing performance data, you can detect underperforming components and take actions such as adjusting server configurations or balancing network loads to enhance overall system efficiency.
- Plan for growth: Monitoring provides valuable insights that aid in strategic planning for future expansion. By understanding current resource usage and performance trends, you can make informed decisions about scaling your infrastructure, such as upgrading hardware or expanding cloud resources, ensuring your system can handle future demands seamlessly.
Key Components of IT Infrastructure
To fully grasp infrastructure monitoring, you need to understand the components it covers:
- Physical components:
- Servers: These are the core machines that handle processing tasks, run applications, and manage data. They include both on-premises servers in your data center and any physical servers used in other locations.
- Network Devices: Routers, switches, and firewalls are essential for managing and directing data traffic across your network. They ensure that data flows efficiently and securely between different parts of your infrastructure.
- Storage Systems: This category encompasses various methods for storing data, ranging from traditional hard drives and network-attached storage (NAS) to modern solid-state drives (SSDs) and storage area networks (SANs). Effective storage management is crucial for data accessibility and performance.
- Virtual components:
- Virtual Machines (VMs): These are software-based emulations of physical computers, allowing multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical server. VMs offer flexibility and scalability for resource management.
- Containers: Containers are lightweight, isolated environments that package applications and their dependencies, making them portable and efficient. They allow for faster deployment and scaling of applications.
- Cloud Services: These include various platforms and services hosted by third-party providers, such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Cloud services provide scalable resources and solutions without the need for on-premises infrastructure.
- Software components:
- Operating systems: Operating systems serve as the fundamental layer upon which all other components of your IT infrastructure are built. They manage hardware resources, enable software applications to run, and provide the essential environment for all IT operations, ensuring that your systems function seamlessly and efficiently.
- Middleware: This software acts as an intermediary between different applications and services, enabling them to communicate and interact effectively. Middleware can include database management systems, message brokers, and other integration tools.
- Applications: Applications are the critical tools that power your business activities. They handle everything from daily operational tasks to complex processes, ensuring that your business runs smoothly. Monitoring these applications is vital to maintaining performance, functionality, and user satisfaction, directly impacting your organization’s success.
Monitoring each of these components provides a holistic view of your infrastructure's health and performance.
How Infrastructure Monitoring Works: Processes and Technologies
Infrastructure monitoring relies on a combination of data collection, analysis, and alerting mechanisms. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Data collection: The process starts with gathering information through agents, APIs, and integrations from various parts of your infrastructure—such as servers, network devices, and storage systems. You can view it as taking each component's 'pulse' to assess its performance. APIs help collect data from external cloud services and third-party apps, while integrations streamline data collection across different platforms.
Metric analysis: Once the data is collected, the next crucial step is metric analysis, where the system processes the information to reveal what's truly happening within your infrastructure. This analysis focuses on three main types of metrics:
- Performance Metrics: Metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and disk I/O provide insights into how hard your systems are working, helping you gauge their efficiency and workload.
- Availability Metrics: Metrics like uptime, response times, and error rates are essential for ensuring that your systems are accessible and operating as expected, helping you quickly identify any disruptions.
- Capacity Metrics: It monitors storage usage, network bandwidth, and resource allocation, giving you a clear understanding of whether your resources are being overused or underutilized. This information is vital for making smart decisions about scaling and managing resources efficiently, helping you avoid both the risks of running out of capacity and the costs of over-provisioning. With a clear view of your resource usage, you can better plan and adjust your infrastructure to meet current and future demands.
Log analysis: Beyond analyzing metrics, monitoring tools also delve into log files, which serve as a detailed diary of your system, capturing every event, error, and anomaly that occurs. These logs provide a chronological record of your infrastructure’s activities, offering deeper insights that go beyond what raw metrics can show. By carefully analyzing these logs, you can identify patterns, trends, or issues that might not be immediately obvious through metrics alone.
SigNoz Logs Event correlation: This is where monitoring gets clever. Advanced systems can connect events happening across different parts of your infrastructure. For example, if your server’s CPU usage suddenly increases and your network slows down at the same time, the system recognizes that these events are related. This connection is crucial for troubleshooting because it helps you understand the bigger picture and identify the underlying cause of problems, rather than just dealing with separate issues one at a time.
Real-time alerting: Finally, you need to know when something goes wrong, and you need to know right away. Monitoring systems set predefined thresholds for various metrics. If any of these thresholds are breached—like if your server's CPU usage suddenly spikes to 100%—the system sends an alert to the relevant team members. This way, you can take action before a minor issue becomes a major problem.
Advanced Monitoring Techniques
Modern infrastructure monitoring goes beyond basic metrics. It employs sophisticated techniques to provide deeper insights:
- AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning provide another level of intelligence to infrastructure monitoring by allowing systems to spot abnormalities and forecast possible problems before they happen. These tools analyze massive volumes of data in real-time, learning what typical behavior looks like and identifying anything strange, such as abrupt increases in resource utilization. This early detection enables you to address problems proactively, rather than reacting after something has already gone wrong. Additionally, machine learning can forecast future issues based on trends, helping you plan and optimize resources more effectively to prevent disruptions.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM) integration: Application Performance Monitoring (APM) integration enhances your monitoring strategy by combining the monitoring of both the infrastructure and the applications running on it. While infrastructure monitoring focuses on the health and performance of physical and virtual components, APM zeroes in on how applications behave and perform within that environment. By integrating these two, you get a more complete and unified view of your system’s overall health. This allows you to not only track the underlying infrastructure but also understand how it directly impacts the applications your business relies on, enabling quicker identification and resolution of issues that span across both layers. To learn more about APM, check out our detailed guide here.
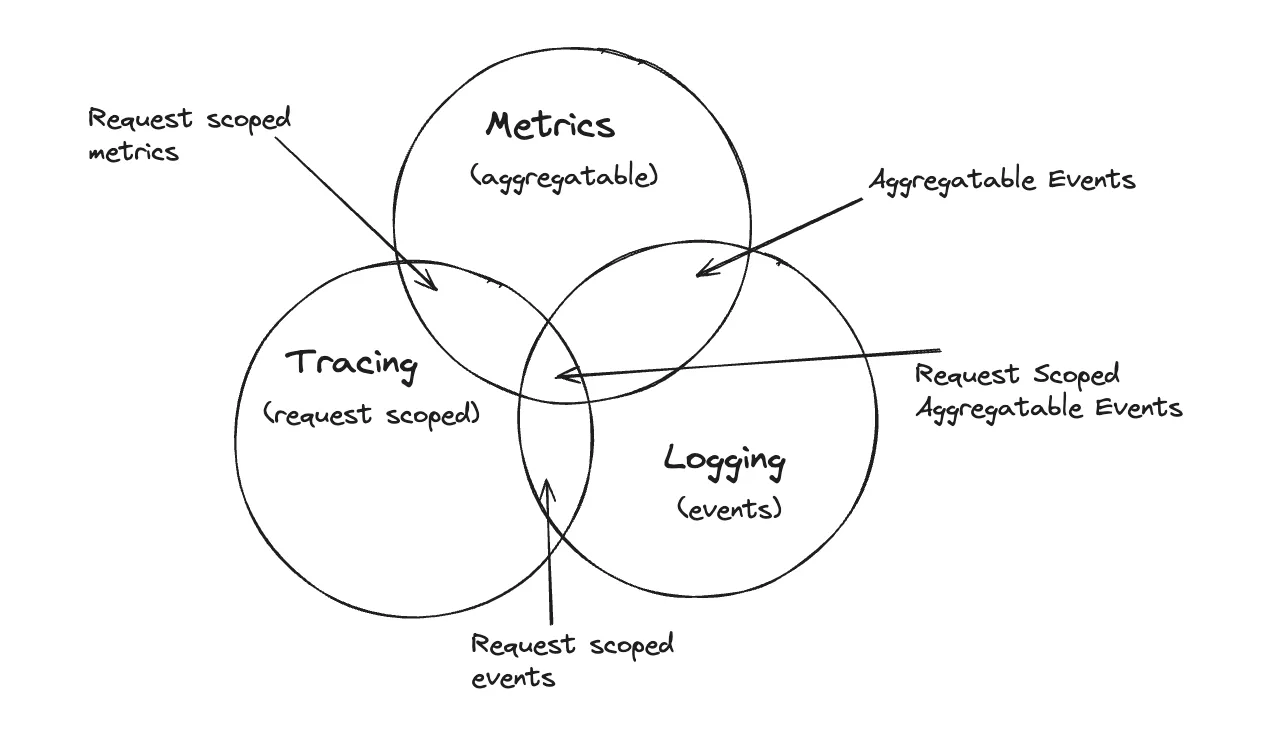
- Observability: Observability takes monitoring a step further by focusing on the ability to understand a system's internal state based on its external outputs, such as logs, metrics, and traces. Unlike traditional monitoring, which often tells you what is happening, observability helps you understand why it's happening by providing deeper insights into the complex relationships and behaviors within your system. This is particularly valuable in modern, distributed environments where systems can be intricate and interdependent. With observability, you can diagnose issues more effectively, uncover the root causes of problems, and gain a comprehensive understanding of how all parts of your system interact and perform.
- Visualization tools: Visualization tools are essential for translating the complex data collected from your infrastructure into something more accessible and actionable. These tools use advanced dashboards and graphs to present data in a visual format, making it easier to digest and understand. By providing clear, visual representations of key metrics and trends, visualization tools help you quickly identify patterns, monitor performance, and track the overall health of your systems. This way, instead of sifting through raw data, you can instantly see what’s happening in your infrastructure and make informed decisions to keep everything running smoothly.
Benefits of Implementing Infrastructure Monitoring
Effective infrastructure monitoring offers numerous advantages:
- Improved system reliability: Comprehensive proactive monitoring empowers you to detect and address potential issues swiftly, thereby enhancing system uptime and service quality consistency. By promptly identifying and resolving problems, you can minimize disruptions, ensuring the reliability and robustness of your systems.
- Enhanced performance: Monitoring tools are adept at identifying performance bottlenecks and inefficiencies within your infrastructure. They analyze metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network throughput to reveal areas where resources may be strained or underutilized. With this detailed insight, you can make targeted adjustments—like reallocating resources or optimizing configurations—to eliminate these inefficiencies. This guarantees that your systems run at optimal efficiency, improving not just the speed of your apps and services but also the entire user experience. By addressing these issues proactively, you help your infrastructure perform at its best, supporting smooth and reliable service delivery.
- Smarter capacity planning: Monitoring data enables you to make informed judgements regarding resource allocation and future growth. Understanding current consumption patterns and trends allows you to plan more efficiently, ensuring you have the necessary resources in place to fulfill demand without overprovisioning.
- Faster incident response: Monitoring systems give real-time warnings and thorough diagnostics, allowing for faster issue detection and response. This prompt reaction minimizes downtime and mitigates the effect of accidents on your company operations.
- Cost optimization: By analyzing resource usage and performance data, you can avoid unnecessary overprovisioning and reduce operational costs. Effective monitoring helps you optimize resource allocation, ensuring you only pay for what you need and reducing wasteful expenditures.
Challenges in Modern Infrastructure Monitoring
Despite its benefits, infrastructure monitoring comes with its own set of challenges:
- Complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments: Managing a combination of on-premises equipment and services distributed across several cloud providers may be difficult. Each environment may have its own monitoring tools, protocols, and configurations, making it difficult to maintain a single picture of the whole infrastructure. Because of the variety of cloud platforms and on-premises systems, integrating numerous monitoring solutions is frequently required, which may be time-consuming and technically challenging.
- Data overload: The amount of data produced by monitoring systems might be daunting. With multiple measurements and logs arriving from various components, it's easy to become lost in a sea of data. The goal is to sort through this data and focus on what is genuinely actionable. Effective monitoring entails discriminating between noise and important insights, and ensuring that the data you act on is relevant and useful for making educated decisions.
- Visibility in containerized environments: Containers, being ephemeral and highly dynamic, pose unique monitoring challenges. Unlike traditional virtual machines, containers can spin up and down quickly, making it harder to track their performance and health over time. Specialized monitoring tools and techniques are needed to manage this transient nature and ensure that you have accurate visibility into containerized applications and services.
- Security integration: Balancing performance monitoring and security concerns adds another level of difficulty. While monitoring solutions prioritize system performance and reliability, incorporating security considerations into monitoring tactics is critical for detecting and responding to possible attacks. Ensuring that performance monitoring does not jeopardize security and vice versa necessitates careful design and the implementation of solutions capable of handling both elements without conflict.
Best Practices for Effective Infrastructure Monitoring
To maximize the benefits of infrastructure monitoring, follow these best practices:
- Align monitoring objectives with business goals: Ensure your monitoring strategy directly supports your organization’s objectives, focusing on the metrics that matter most.
- Implement comprehensive coverage: Monitor all layers of your infrastructure, including physical, virtual, and cloud environments, to gain a complete understanding of your system’s health.
- Leverage automation: Utilize automated tools for routine monitoring tasks and alert management, allowing your team to focus on more complex issues.
- Continuously refine processes: Regularly review and update your monitoring approach to adapt to evolving infrastructure needs and technologies.
- Foster a culture of observability: Encourage teams to prioritize monitoring and use data-driven insights for decision-making, enhancing system reliability and performance.
- Establish Clear Metrics and KPIs: Define specific, actionable metrics and key performance indicators that align with your business goals, ensuring that monitoring efforts are focused and effective.
- Ensure Scalability: Design your monitoring systems to scale with your infrastructure, accommodating growth without compromising performance or visibility.
- Tune Alerts for Relevance: Optimize alert thresholds and notifications to minimize noise and ensure that only critical issues demand immediate attention.
- Prioritize Security: Incorporate security monitoring into your infrastructure strategy, ensuring that performance and security considerations are balanced.
- Integrate with Incident Management: Link your monitoring tools with incident tracking systems to streamline issue resolution and improve response times.
Leveraging SigNoz for Advanced Infrastructure Monitoring
To effectively monitor Infrastructure, using an advanced observability platform like SigNoz can be highly beneficial. SigNoz is an open-source observability tool that provides end-to-end monitoring, troubleshooting, and alerting capabilities for your applications and infrastructure.
Here's how you can leverage SigNoz for Infrastructure Monitoring solutions:
- Create a SigNoz Cloud Account
SigNoz Cloud provides a 30-day free trial period. This demo uses SigNoz Cloud, but you can choose to use the open-source version.
- Using SigNoz Infrastructure Monitoring:
In the top left corner, click on Get Started.
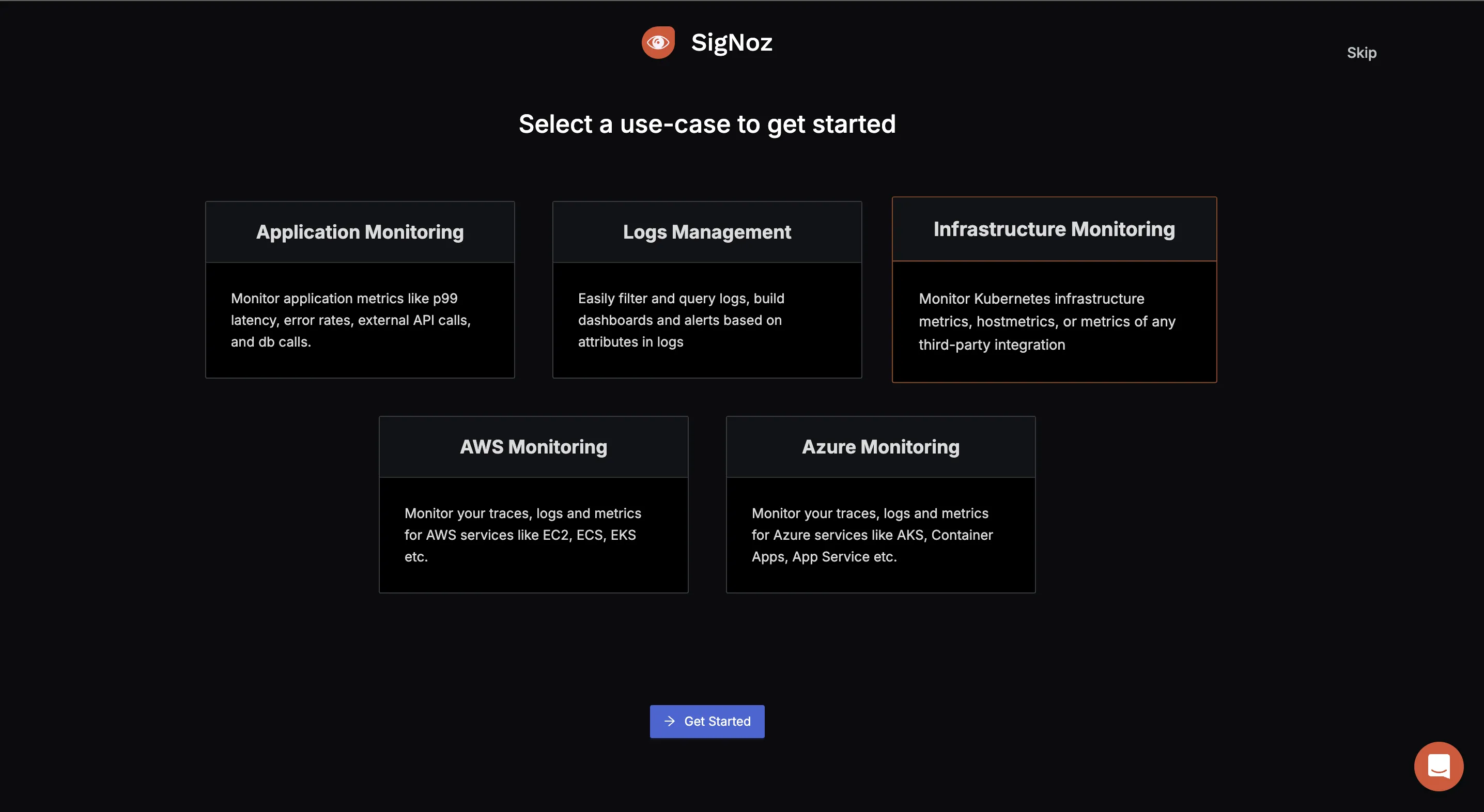
You will be redirected to “Get Started Page”. Choose Infrastructure Monitoring
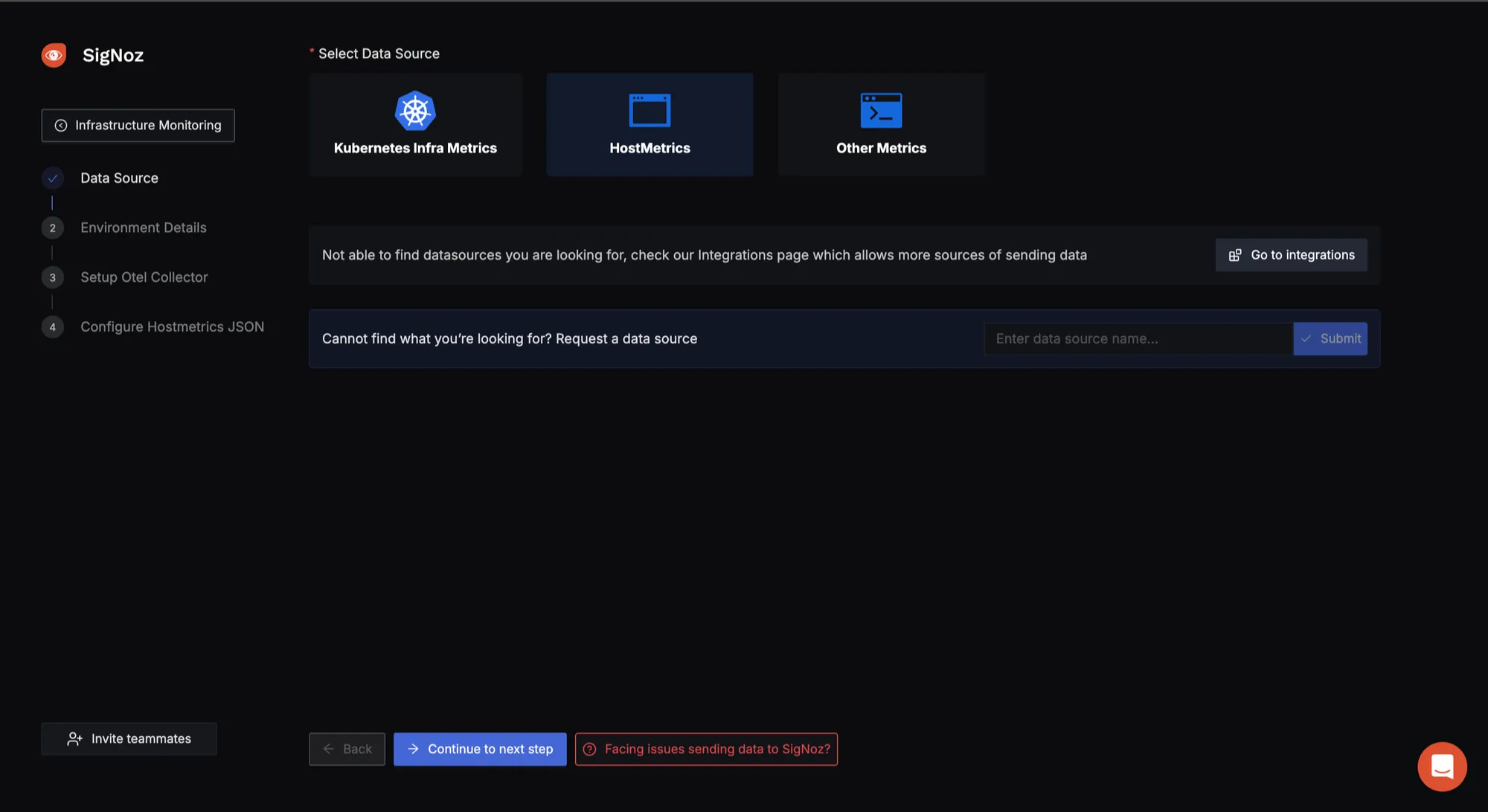
- Select Data Source:
You need to select the Data Source. Since the metrics to be collected here are from the host system, select HostMetrics.
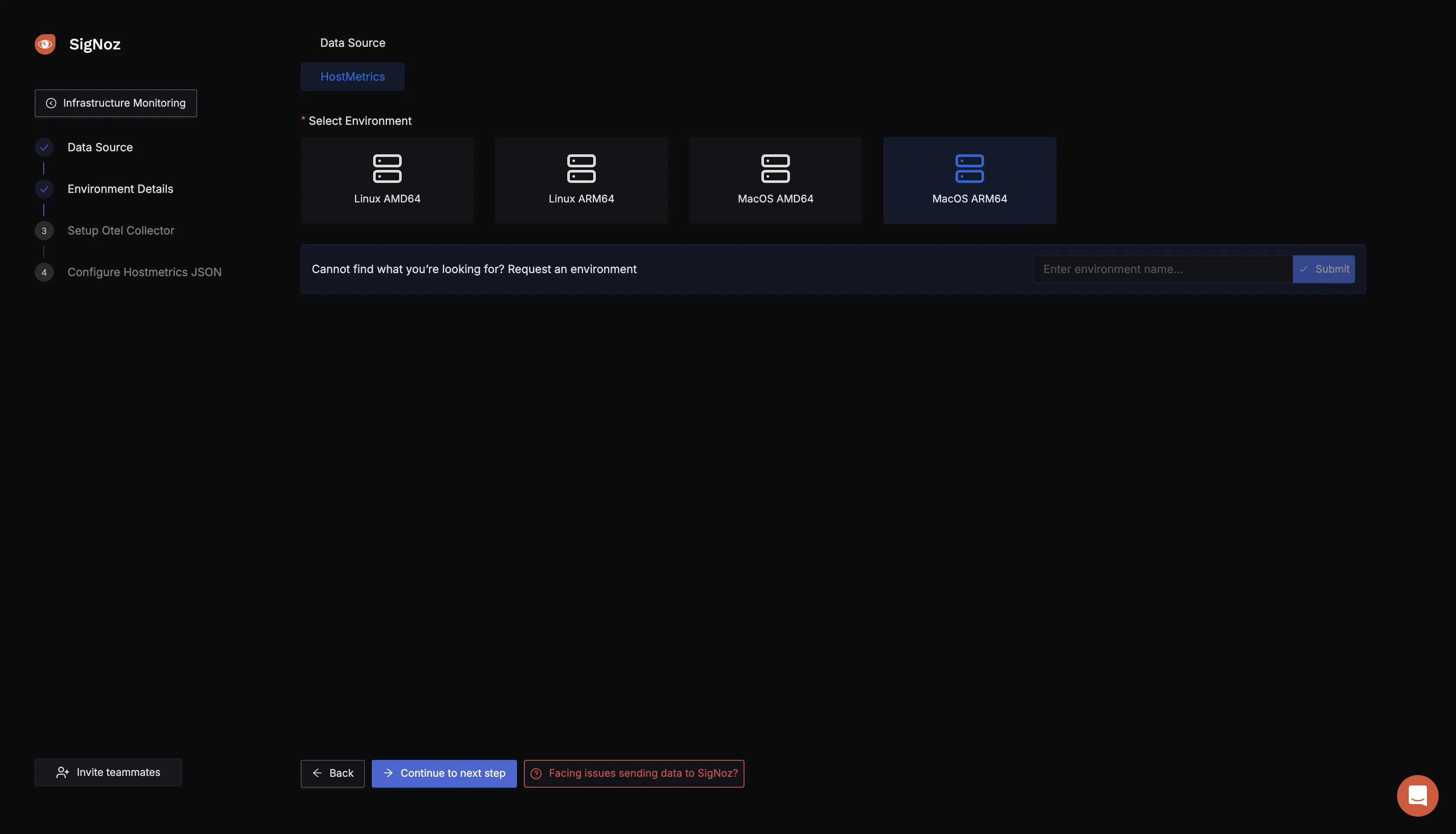
Choose the environment of your host system. For this demo, I am using my laptop which is a Macbook M1.
- Setup OTel Collector as an agent
Follow the steps in the SigNoz Cloud section of this tutorial to get your Otel Collector agent up and running.
Note: Download the latest version of the Otel Collector that matches your host operating system.
- Configure the Host Metrics Dashboard
To send host metrics to SigNoz, refer to the documentation for detailed instructions.
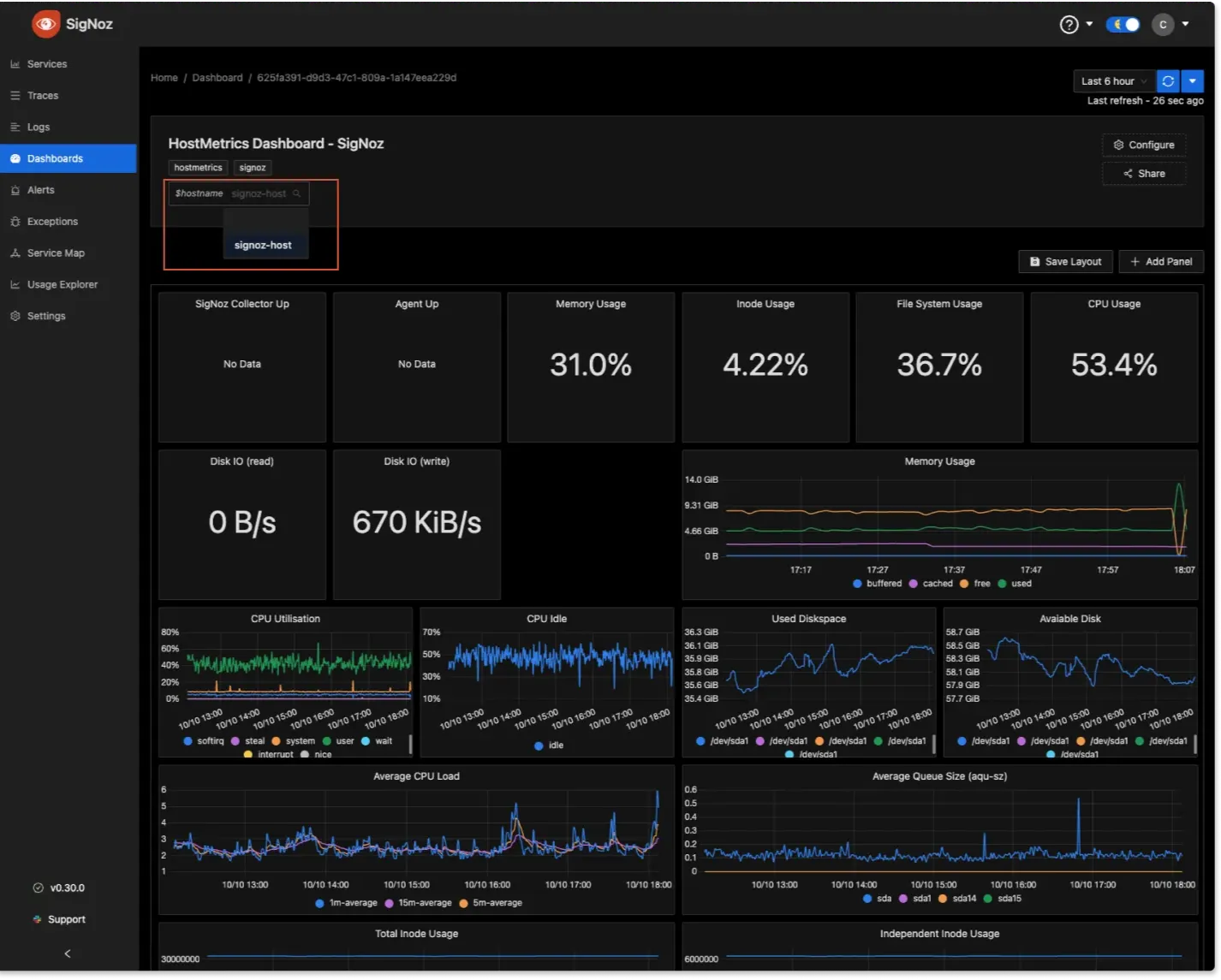
To explore more dashboard functionalities, check out the Dashboard Section.
Key Takeaways
- Infrastructure monitoring is critical for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of your IT environment, from physical servers to cloud services.
- Effective monitoring covers physical components (servers, network devices, storage systems), virtual components (VMs, containers, cloud services), and software components (operating systems, middleware, applications).
- Proactive monitoring helps prevent downtime, optimize performance, and plan for future growth, providing a reliable and scalable infrastructure.
- Modern infrastructure monitoring leverages AI, machine learning, and observability to detect issues early and understand complex system behaviors.
- Managing hybrid and multi-cloud environments, handling data overload, ensuring visibility in containerized environments, and integrating security are key challenges in infrastructure monitoring.
- Align monitoring with business goals, ensure comprehensive coverage, use automation, continuously refine processes, and prioritize security and scalability.
FAQs
What's the difference between infrastructure monitoring and application monitoring?
Infrastructure monitoring focuses on the health and performance of the underlying systems—like servers and networks—that support your applications. It ensures the environment is stable and efficient. In contrast, application monitoring targets the software itself, tracking how well the application performs and behaves from the user’s perspective. While infrastructure monitoring looks after the foundation, application monitoring ensures the applications on that foundation run smoothly.
How often should infrastructure monitoring checks be performed?
The frequency of infrastructure monitoring checks depends on your specific needs. However, most systems benefit from continuous monitoring with real-time or near-real-time updates for critical components to quickly identify and address potential issues.
Can infrastructure monitoring help with cost optimization in cloud environments?
Yes, infrastructure monitoring can help with cost optimization in cloud environments. By providing insights into resource usage and performance, it enables you to identify over-provisioned resources and adjust them to optimize your cloud spending.
What are some common infrastructure monitoring metrics to track?
Common metrics to track include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, network throughput, error rates, and response times. The specific metrics you monitor will depend on your infrastructure and business requirements.
